2020-03-08 by Quick Biology Inc.
CUT&RUN (cleavage under targets and release using nuclease) is an epigenomic profiling method developed by the group of Dr. Steven Henikoff at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center (ref1,2). CUT&RUN is performed in situ on immobilized, intact cells without crosslinking. DNA fragmentation is achieved using micrococcal nuclease fused to Protein A and/or Protein G (pA/G-MNase). The fusion protein is directed to the desired target through binding of the Protein A/G moiety to the Fc region of an antibody bound to the target. DNA under the target is subsequently cleaved and released and the pA/G-MNase-antibody-chromatin complex is free to diffuse out of the cell. DNA cleavage products are extracted and then processed by next generation sequencing (NGS) (Fig.1, ref1,2,3,4). This protocol gives many advantages:
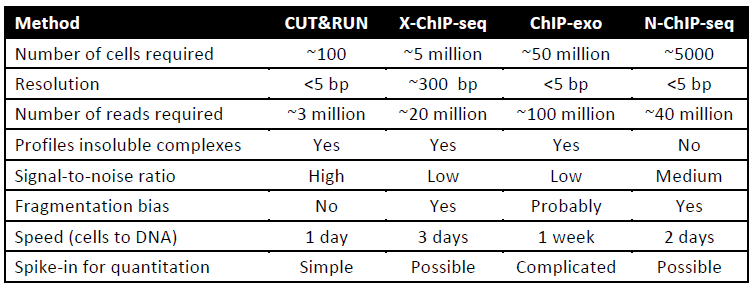
- - requires fewer cells (see in Table)
- - lower noise (background peaks in Fig.2), lower sequencing depths needed
- - faster workflow (less 2 days)
Figure 1: CUT&RUN protocol pipeline. Nuclei attached to magnetic beads can be treated successively with an antibody (or optionally with a primary and secondary antibody) and Protein A-MNase (pA-MN), which diffuse in through the nuclear pores. After Ca++ addition to activate MNase cleavage, fragments are released and diffuse out of the nucleus. DNA extracted from the supernatant is used to prepare libraries for paired-end sequencing.
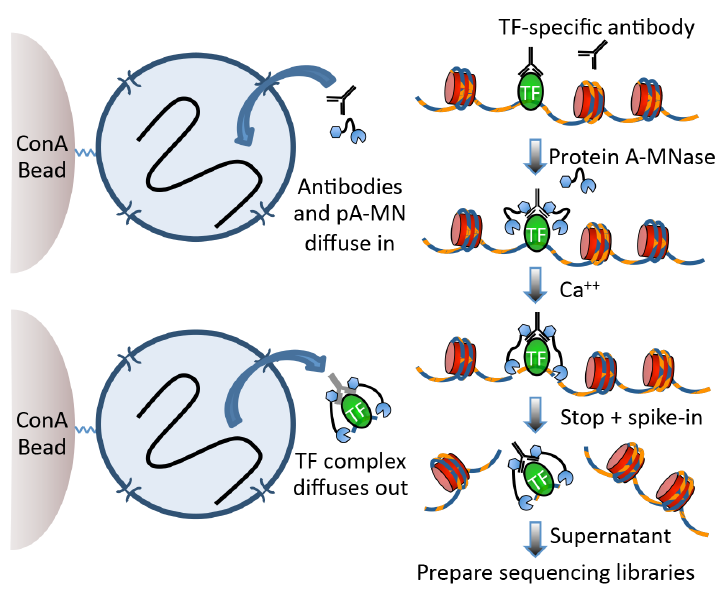
Figure 2: Higher resolution, lower cell number requirement using CUT&RUN protocol. CUT&RUN of H3K27me3 requires only 100 cells to profile the human Polycomb chromatin landscape. A varying number of K562 cells was used as the starting material for profiling H3K27me3 by CUT&RUN. Following paired-end 25x25 bp Illumina sequencing and removal of duplicates, 7.5 million reads were randomly selected and used to generate bedgraphs representing raw counts, as indicated on the y-axis. For comparison, ENCODE XChIP-seq data (GSM733658) was similarly analyzed.
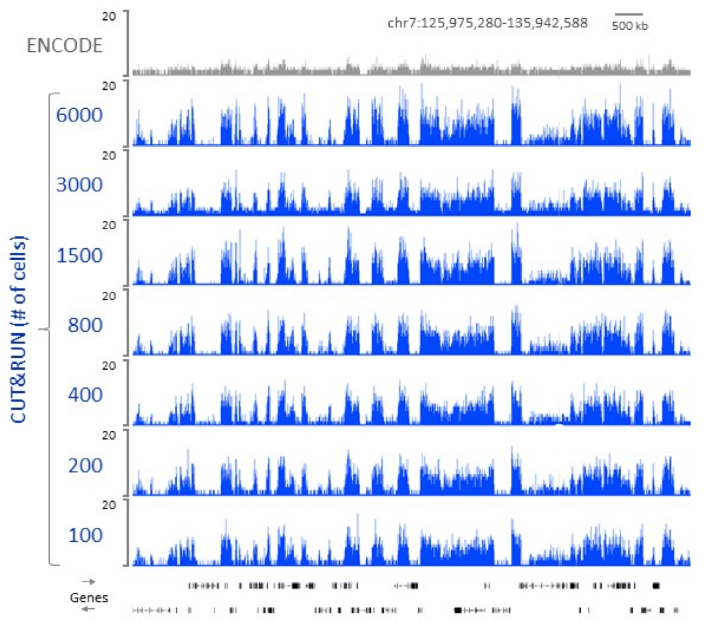
Table: Comparison of CUT&RUN to ChIP-seq protocols
Quick Biology is an expert in using NGS for epigenetic. We are providing both ChIP-seq and CUT&RUN services. Find More at Quick Biology.
Ref:
- 1. Skene, P. J., Henikoff, J. G. & Henikoff, S. Targeted in situ genome-wide profiling with high efficiency for low cell numbers. Nat. Protoc. 13, 1006–1019 (2018).
- 2. Meers, M. P., Bryson, T. D., Henikoff, J. G. & Henikoff, S. Improved cut&run chromatin profiling tools. Elife 8, 1–16 (2019).
- 3. EpiCypher: https://www.epicypher.com/cutana
- 4. Antibodies-online Inc.: https://campaigns.antibodies-online.com/cutandrun-sets/?gclid=EAIaIQobChMIuf7T173a5wIVkuNkCh0uZg_oEAAYASAAEgLOyPD_BwE