- R&D
- Clinical Diagnosis
- News
- Company
QuickBiology News
News Center
Here are relevant industry news and updates on our company
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common clinical condition associated with diverse etiologies and abrupt loss of renal function. Read More
Core regulatory circuitry (CRC)-dependent transcriptional network is critical for developmental tumors in children and adolescents carrying few gene mutations. Read More
Genomic
Gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas (GIAC) of the tubular gastrointestinal (GI) tract including esophagus, stomach, colon, and rectum comprise most GI cancers and share a spectrum of genomic features. Read More
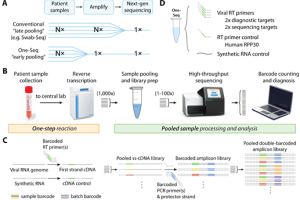
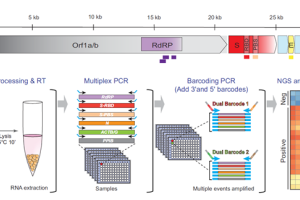
NGS-based SARS-CoV-2 virus detection not only eliminates bottlenecks in scalability but also identifies viral variants, which plays a big role in current SARS-CoV2 VOC (Variants of concerns) surveillance. Previously, Quick Biology reported several scientists’ works, that followed traditional barcoding and sequencing workflows, and required individual RNA extraction and PCR thermocycling steps. In recent medRxiv, researchers from Harvard Medical School reported a new method “One-Seq”, that eliminates the current bottlenecks in scalability by enabling early pooling of samples, before any extraction or amplification steps. Read More
Chromatin packing and histone modification are important factors for gene regulation. ATAC-seq (Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin using sequencing), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-seq are typical methods for chromatin accessibility and histone modifications. While the genomic profiles of various chromatin and histone modifications have been extensively characterized at the bulk cells, biotech is now at the stage of single-cell resolution.Read More
Gut microbiota lives in our digestive tracts and is established at birth. Initial research suggests certain bacteria in our gut can prevent and treat many common diseases, such enormous system of organisms’ influences, improves our health conditions. Understanding how population changes or evolves of gut microbiota in our body in development is fundamental, critical, but challenging as trillions of gut bacteria in ~ 1,000 different species in our body.Read More
Multiplex detection is the test that numerous analyte targets and internal controls are conducted simultaneously in one reaction. In nucleic acid detection, the gold standard RT-qPCR is multiplexable, which uses the TaqMan method that each target probe is labeled by different fluorescence. The benefits of multiplexing not only reduce reaction costs by at least 50% but also give “self-calibrated” data as all analytes are conducted in the same reaction.Read More
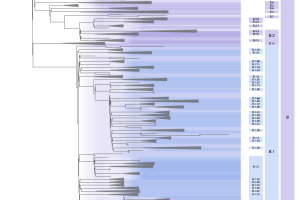
The ongoing pandemic of SARS-CoV-2 has resulted in the generation of hundreds of thousands of virus genome sequences, as of Feb 3, 2021, 468,000 sequences of SARS-CoV-2 from COVID-19 patients have been uploaded into public databases. A rational and dynamic virus nomenclature uses a phylogenetic framework to identify lineages. Read More
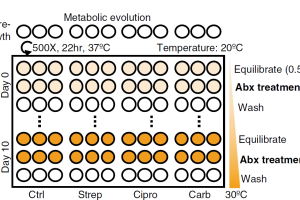
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a serious public health concern, especially in Asian countries due to antibiotic overuse. The mechanism of antibiotic resistance is complex but is generally grouped into three broad categories: target modification, drug inactivation, and drug transport. Read More
As people in the U.S. are receiving the vaccine for SARS-CoV-2, the pandemic slows down. In many states, public schools plan back to normal. High throughput virus test before back to work, full day-in person school learning is critical for controlling any future spread of SARS-CoV-2.Read More